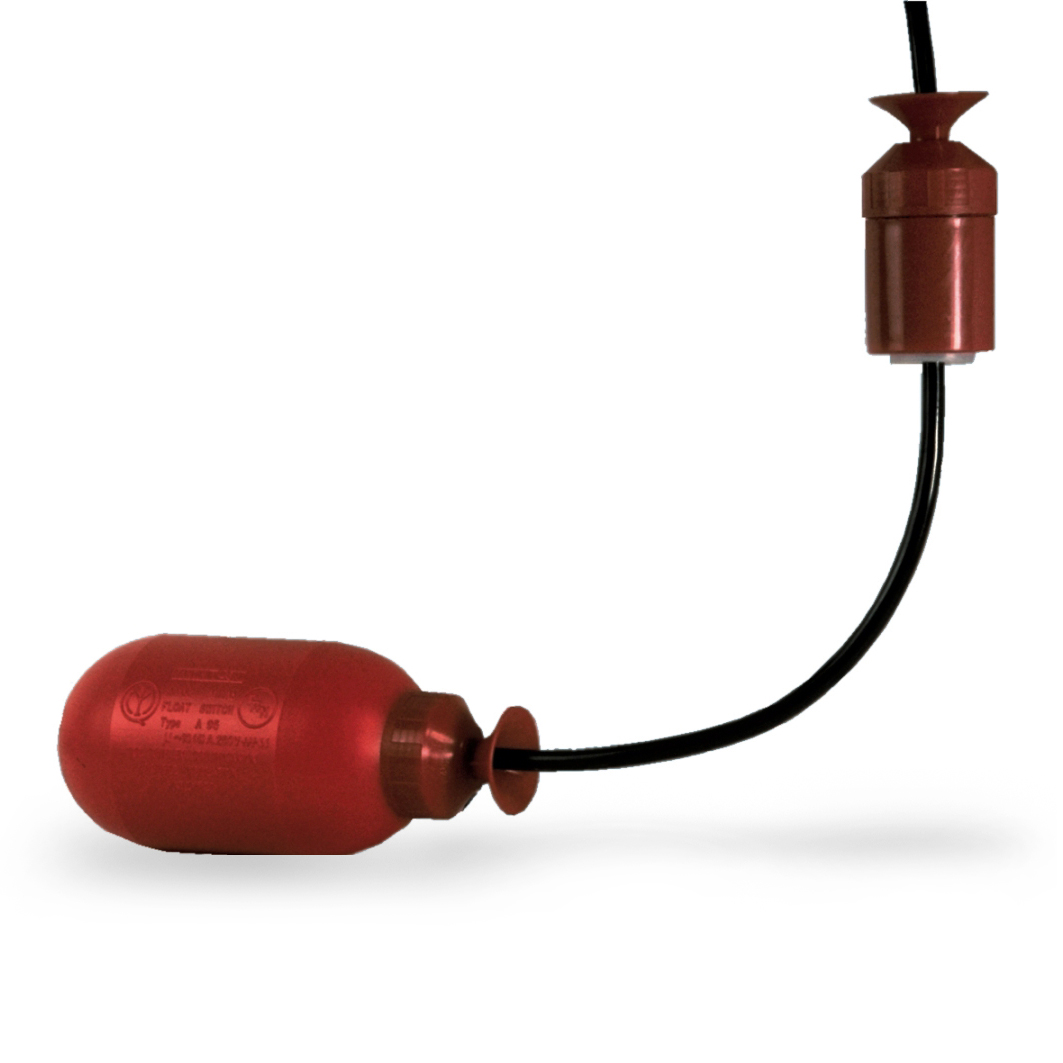
Electromechanical submersible level controls for open tanks
-
DESCRIPTION
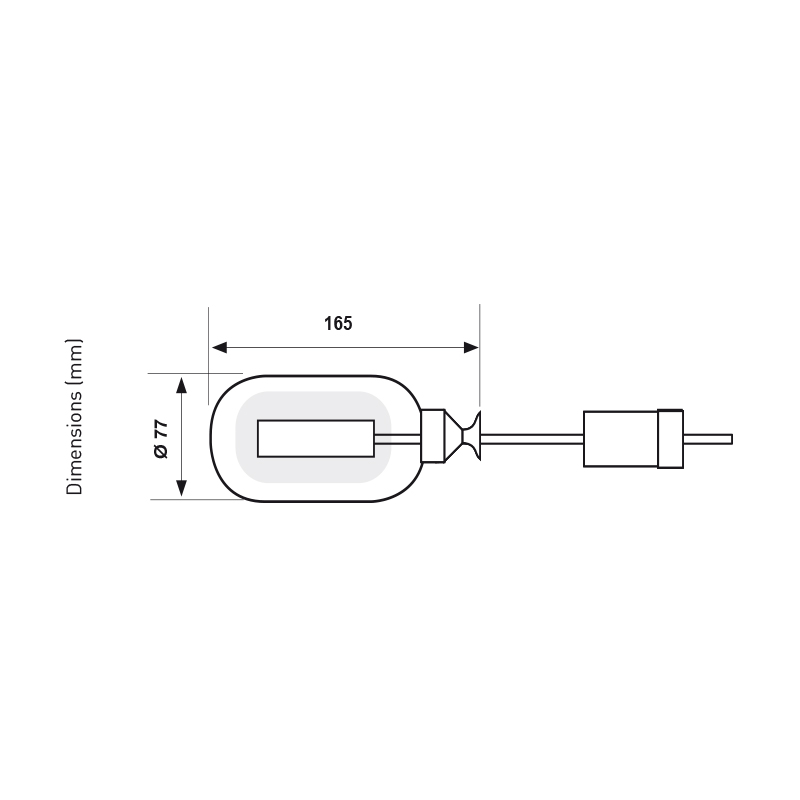
General features0
Suitable for monophase pumps with direct control to adjust levels of clear or contaminated water, acid or alkaline aqueous solutions of any density. Do not use for ketonic and aromatic hydrocarbons.
- Blow moulded moplen outer casing, chemical resistant and shockproof.
- Intermediate casing filled with polyurethane foam.
- In the inner side is located a two-channel electrical device with two positions.
- Working area of the electrical device is made of lead to prevent blocking and oxidation.
- Adjustable counterweight position to select the level differential.
- Moplen blow moulded cable gland on the electrical cable.
- Double insulation.
- Test class: II.
- Storage and transport temperature: -25 ÷ 60°C.
- A95A Unit weight 0.7 Kg.
- A95B Unit weight 1.3 Kg.
Electric features- Electrical SPDT switch with one way and 2 positions.
- Electrical cable type AØ5VV-F 3×1 RF60 CEI-UNEL 35746.
- Double insulation: 4kW.
-
ADVANTAGES
0
Suitable for monophase pumps with direct control to adjust levels of clear or contaminated water, acid or alkaline aqueous solutions of any density. Do not use for ketonic and aromatic hydrocarbons.
Advantages -
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION
CODE CABLE TYPE CABLE LENGTH MT CONTACTS RATING MAXIMUM PRESSURE PROTECTION DEGREE A95A PVC 3 10(4)A 250Vca 60 °C IP68 A95AS1 PVC 5 10(4)A 250Vca 60 °C IP68 A95B PVC 10 10(4)A 250Vca 60 °C IP68 A95BS1 PVC 15 10(4)A 250Vca 60 °C IP68 A95AS2 * neoprene 3 10(4)A 250Vca 45 °C IP68 A95AS3 * neoprene 5 10(4)A 250Vca 45 °C IP68 A95BS4 * neoprene 10 10(4)A 250Vca 45 °C IP68 A95BS5 * neoprene 15 10(4)A 250Vca 45 °C IP68 A95BS6 * neoprene 20 10(4)A 250Vca 45 °C IP68 A95BS7 * neoprene 25 10(4)A 250Vca 45 °C IP68 * delivery time and minimum purchase quantity upon request -
HOMOLOGATION AND INSTALLATION
Homologation
- Conformity with EN 60730-1, 60730-2-16.
- Homologation TÜV
Installation and use- Suitable for water
- Waterproof float
- Level control by mean of floats to be made by setting the counterweight position
- TECHNICAL LITERATURE
-
FAQS