Antifreeze heating cables with constant power for pipes
-
DESCRIPTION
General features0
Suitable for protection against freezing pipes for misting, irrigation and fire prevention systems
Constant power delivered ~10 W/m
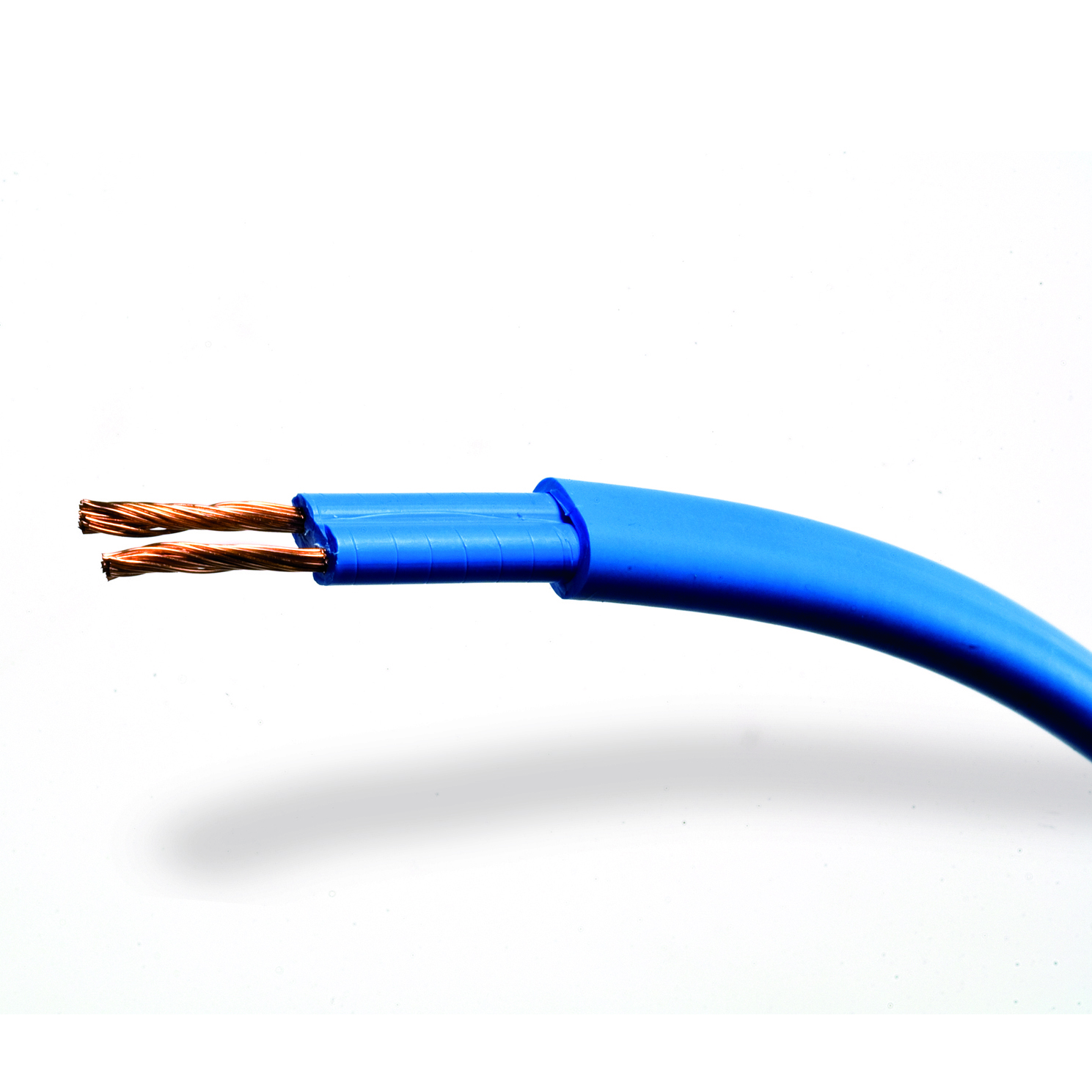
- Cable composition:
– 2 conductors x 1.5 mm²
– PVC sheath
– Nickel-chromium heating element
– Internal splicing point
– Silicone insulation - Maximum room temperature powered 40 °C
- Minimum installation room temperature -20 °C
- Minimum storage room temperature -20 ÷ -25°C
- Maximum length of the heating circuit from the supply point 160 m
Electric features- Power supply 230V-50Hz
- Constant power delivered ~10W/m
- Cable composition:
-
ADVANTAGES
0
Suitable for protection against freezing pipes for misting, irrigation and fire prevention systems
Constant power delivered ~10 W/m
Advantages -
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION
CODE CABLE LENGTH MINIMUM INSTALLATION TEMPERATURE MAXIMUM TEMPERATURE POWERED MAXIMUM LENGHT OF HEATING CIRCUIT FROM SUPPLY POINT K12C25 25 m -20 °C 40 °C 160 m K12C50 50 m -20 °C 40 °C 160 m K12C75 75 m -20 °C 40 °C 160 m -
HOMOLOGATION AND INSTALLATION
Homologation
- CE
Installation and use- The cable can only be cut at the indicated splicing points;
- Minimum bending radius 20 mm;
- The length of the cable varies according to the diameter of the pipe;
- The cable must be secured along the pipe with the relevant fixing tape code K50 for steel pipes or code K50AL for plastic pipes;
- In the case of large pipes, the strips may need to be wound so as to ensure adequate heat;
- The conductors have cold tails and can be connected directly to the thermostat or to the junction box;
- At the end of the cable, the 2 conductors must be kept insulated and must not come into contact with each other; use the kit to seal the terminals for cables with constant power (for 1 cable) code KIT1A;
- It is advisable to apply an insulating coating over the heating cable for a correct installation;
- Refer to the table to check whether the cables must be wound in a spiral with an increase in the required length.
- The heating cables consist of a coil-wound resistance on two conductors. The resistance is in contact with the conductors through splicing points at constant intervals; the energy to heat the resistance is drawn at the splicing points;
- The total power of the cable is determined by a combination of temperature, length of the heating circuit and supply voltage;
- They require control thermostats to be used to function.
ACCESSORIES
- Code KBE3A: junction box in insulating material;
- Code KSUPP-A: support foot for the KBE3A junction box;
- Code K50: fiberglass fixing tape for metal pipes;
- Code K50AL: fixing tape for plastic pipes;
- Code KIT1A: kit to seal terminals for cables with constant power (for 1 cable);
- Code KFAN: labels for the presence of a heating cable;
- Code L03BM1A: ON/OFF Thermostat – proportional – P.I.D. at 1 outlet;
- Code C03A3: immersion thermostat for pipes.
- TECHNICAL LITERATURE
-
FAQS